Android: Agent Smith
Original Issue Date:-
July 11, 2019
Virus Type:-
Trojan
Severity:-
High
It has been observed that a new malware named as “Agent Smith” targeting android devices is spreading widely. The malware has the capability to automatically replace the installed apps of the infected/targeted device to malicious versions without the user knowledge. It has also been counted that the malware has infected nearly 25 million mobile devices all over the world. The malware mainly spreads by installing apps from third party app stores, 9Apps and targets the Hindi, Arabic, Russian and Indonesian speaking users. The malware is capable of performing the following functions:
- Exploits Android vulnerabilities and thereafter replace installed apps with malicious versions.
- Displays fake ads for financial gains, stealing banking credentials and for eavesdropping.
- Has similar features related to Gooligan, HummingBad, and Copycat malwares.
- Make use of android security environment loopholes such as Janus, Bundle and Man-in-the-Disk to build a 3-stage infection chain.
- Hide its icon from the launcher and impersonates as legitimate app.
Working
The malware works in 3-stage infection chain which is:
- Victims are lured to install dropper apps such as photo utility, games etc, containing weaponized Feng Shui Bundle as encrypted asset files.
- Dropper decrypts itself to install its core malware APK file which impersonates itself as Google Updater, Google Update for U or “com.google.vending”. This APK is capable of performing malicious patching and updating apps.
- The malicious apk checks for the installed apps and compare it with the list of targeted apps (hardcoded/sent from CnC server). If any of the installed apps matches with the list of targeted apps then its apk is extracted and its code is modified with the malicious code and that app is reinstalled in the name of App update.
The list of malicious apps which is hardcoded in the malware is given below.
- lenovo.anyshare.gps
- mxtech.videoplayer.ad
- jio.jioplay.tv
- jio.media.jiobeats
- jiochat.jiochatapp
- jio.join
- good.gamecollection
- opera.mini.native
- startv.hotstar
- meitu.beautyplusme
- domobile.applock
- touchtype.swiftkey
- flipkart.android
- cn.xender
- eterno
- truecaller
The list given above is updated on regular basis by fetching from command and control server. If communication fails, then it uses the default list of apps hardcoded in the malware.
Malicious Apps
Initial Dropper Apps:
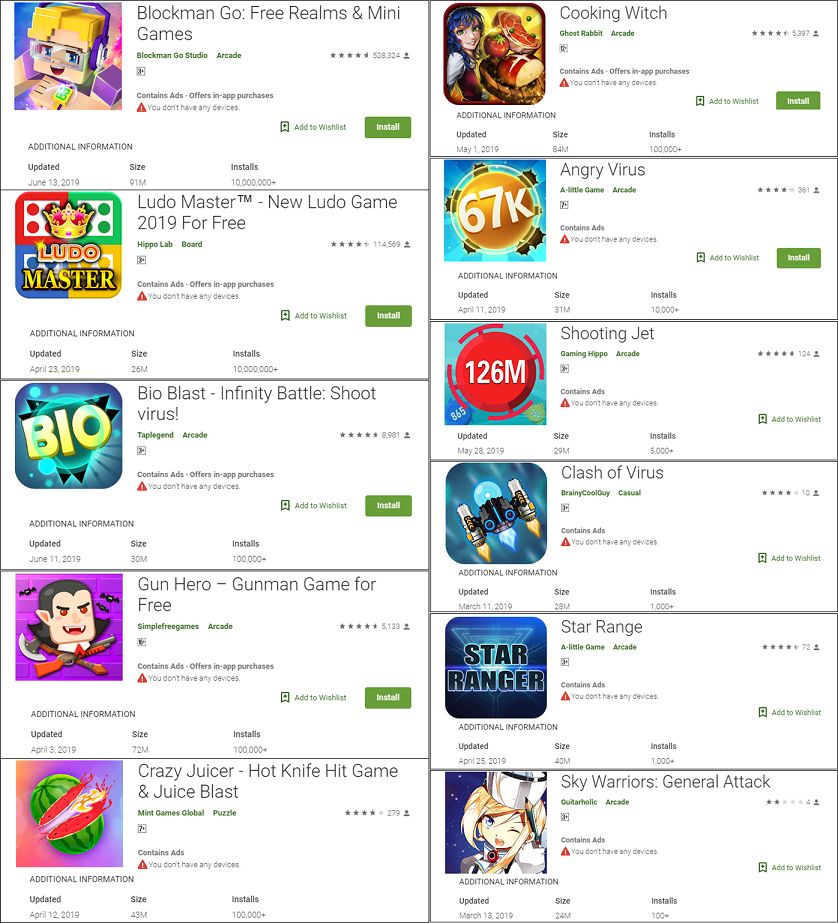
The top 5 most infectious droppers downloaded more than 7.8 million times are given below:
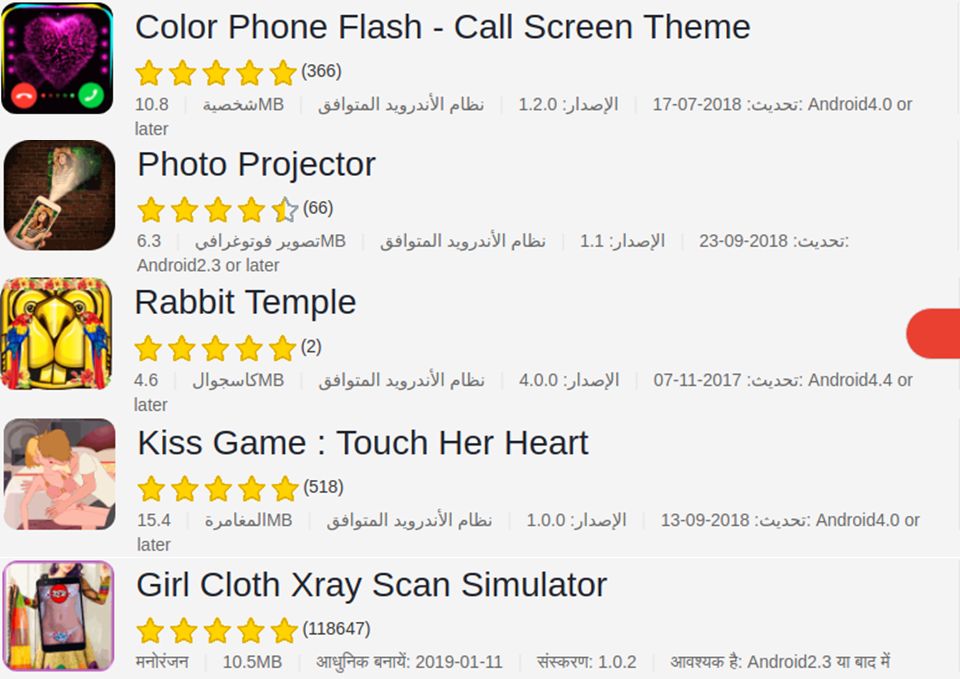
Some of the malicious apps that were infected by the malware is given below. Currently these apps were removed from the Google Play store.
Countermeasures:
- If you have been infected by Apps such as those mentioned above, kindly uninstall it and if required, reinstall the apps from authentic app stores.
- Do not download and install applications from untrusted sources [offered via unknown websites/ links on unscrupulous messages]. Install applications downloaded from reputed application market only.
- Install and maintain updated antivirus solution on android devices. Scan the suspected device with antivirus solutions to detect and clean infections.
- Prior to downloading / installing apps on android devices (even from Google Play Store), Always review the app details, number of downloads, user reviews, comments and "ADDITIONAL INFORMATION" section.
- Verify app permissions and grant only those permissions which have relevant context for the app's purpose.
- In settings, do not enable installation of apps from "Untrusted Sources".
- Exercise caution while visiting trusted/untrusted sites for clicking links.
- Install Android updates and patches as and when available from Android device vendors.
- Users are advised to use device encryption or encrypting external SD card feature available with most of the android OS.
- Do not download or open attachment in emails received from untrusted sources or unexpectedly received from trusted users.
- Avoid using unsecured, unknown Wi-Fi networks. There may be rogue Wi-Fi access points at public places used for distributing malicious applications.
- Confirm that the banking app you’re using is the official, verified version.
- If anything looks awry or suddenly unfamiliar, check in with your bank’s customer service team.
- Use two-factor authentication if it’s available.
- Make sure you have a strong AI-powered mobile antivirus installed to detect and block this kind of tricky malware if it ever makes its way onto your system.
- Refer to security best practices for mobile Phone users:
http://www.cyberswachhtakendra.gov.in/documents/Mobile_phone_Security.pdf
References:
- https://www.checkpoint.com/press/2019/25-million-infected-devices-check-point-research-discovers-new-variant-of-mobile-malware/#
- https://research.checkpoint.com/agent-smith-a-new-species-of-mobile-malware/
- https://www.theverge.com/2019/7/10/20688885/agent-smith-android-malware-25-million-infections
- https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/25-million-android-devices-infected-by-agent-smith-malware/
- https://thenextweb.com/security/2019/07/10/agent-smith-malware-replaces-legit-android-apps-with-fake-ones-on-25-million-devices/
- https://www.firstpost.com/tech/news-analysis/agent-smith-malware-replaces-android-apps-with-fake-ones-on-25-million-devices-6973031.html


