Proxyware / Notepad++-Disguised Malware
Original Issue Date:-
February 13, 2026
Virus Type:- Proxyware
Severity:-
Medium
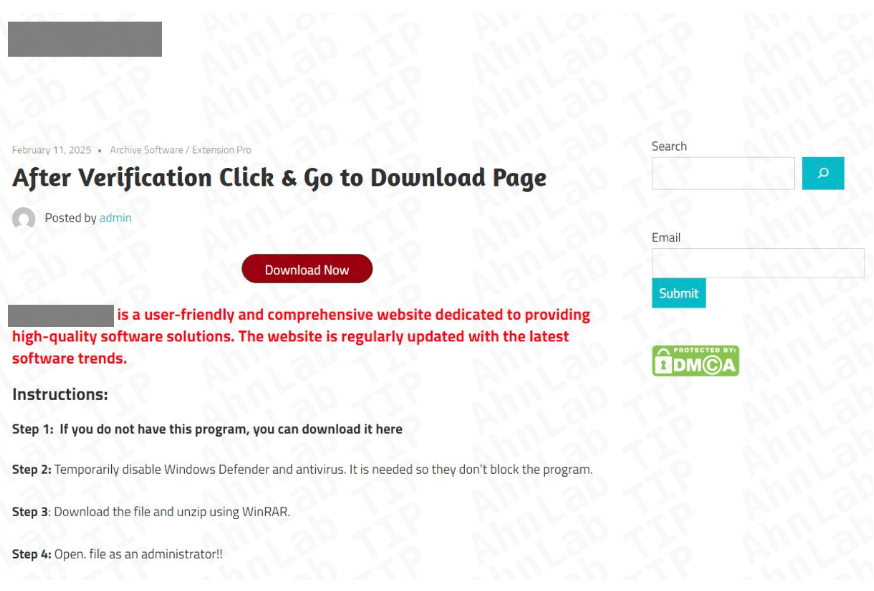
It has been reported that a proxyware/Notepad++-disguised malware is being distributed through a malicious campaign in which threat actors spread malware disguised as a Notepad++ installer or other utility installers (e.g., cracked software) via deceptive download portals and advertisements. In this proxyjacking attack, the malware installs proxyware components on the victim system without consent, allowing the attacker to hijack the system’s network bandwidth and share it with external networks for profit.
Infection Mechanism:
The attackers leverage deceptive download sites, malicious advertisements, cracked software portals and manipulated distribution channels to deliver trojanized installer packages. The infection typically begins when users download a malicious installer such as Setup.msi or compressed archives like Setup.zip from unofficial or compromised sources. Once executed, the malicious installer (e.g., “Setup.msi” or the ZIP archive “Setup.zip”) can register itself as scheduled tasks such as “Notepad Update Scheduler” and persistently deploy additional malware components. These components include loaders like DPLoader, which in turn deploys proxyware modules such as Infatica and DigitalPulse on the infected system. The malware uses PowerShell scripts to install NodeJS, decrypt embedded payloads, create obfuscated JavaScript or Python-based DPLoader files and register persistence mechanisms via Windows Task Scheduler. The infected system may experience unauthorized network bandwidth usage, communication with attacker-controlled command-and-control (C2) infrastructure and potential secondary payload execution, representing a risk of covert resource abuse and further compromise.
Indicator of Compromise:
MD5 Hashes:- 01f6153a34ab6974314cf96cced9939f
- 05e27d1d0d1e24a93fc72c8cf88924f8
- 0fe7854726d18bbc48a5370514c58bea
- 171e48e5eeae673c41c82292e984bac9
- 18c1e128dbfe598335edb2ce3e772dd1
- Scheduled Tasks: UNBScheduler, UNPScheduler, Notepad Update Scheduler
- Setup.msi
- Setup.zip
- TextShaping.dll
- infatica_agent.dll
For more detailed list of IoC, kindly refer the below URLs:
Best Practices and Recommendations:
- Do not download and install applications from untrusted sources [offered via unknown websites/ links on unscrupulous messages]. Install applications downloaded from reputed application market only. Users must be aware while clicking on links during web search.
- Update software and operating systems with the latest patches. Outdated applications and operating systems are the targets of most attacks.
- Avoid running commands or downloading files presented during CAPTCHA checks, particularly if asked to perform tasks outside your web browser.
- Don't open attachments in unsolicited e-mails, even if they come from people in your contact list, and never click on a URL contained in an unsolicited e-mail, even if the link seems benign. In cases of genuine URLs close out the e-mail and go to the organization’s website directly through browser
- It is advised to block office applications from creating executable files.
- Install ad blockers to combat exploit kits such as Fallout that are distributed via malicious advertising.
- Prohibit external FTP connections and blacklist downloads of known offensive security tools.
- All operating systems and applications should be kept updated on a regular basis. Virtual patching can be considered for protecting legacy systems and networks. This measure hinders cybercriminals from gaining easy access to any system through vulnerabilities in outdated applications and software. Avoid applying updates / patches available in any unofficial channel.
- Restrict execution of Power shell /WSCRIPT in an enterprise environment. Ensure installation and use of the latest version of PowerShell, with enhanced logging enabled. Script block logging and transcription enabled. Send the associated logs to a centralized log repository for monitoring and analysis. https://www.fireeye.com/blog/threat-research/2016/02/greater_visibilityt.html
- Establish a Sender Policy Framework (SPF) for your domain, which is an email validation system designed to prevent spam by detecting email spoofing by which most of the ransomware samples successfully reaches the corporate email boxes.
- Application whitelisting/Strict implementation of Software Restriction Policies (SRP) to block binaries running from %APPDATA% and %TEMP% paths. Ransomware sample drops and executes generally from these locations.
- Users are advised to disable their RDP if not in use, if required, it should be placed behind the firewall and users are to bind with proper policies while using the RDP.
- Block the attachments of file types, exe|pif|tmp|url|vb|vbe|scr|reg|cer|pst|cmd|com|bat|dll|dat|hlp|hta|js|wsf
- Consider encrypting the confidential data as the ransomware generally targets common file types.
- Perform regular backups of all critical information to limit the impact of data or system loss and to help expedite the recovery process. Ideally, this data should be kept on a separate device, and backups should be stored offline.
- Network segmentation and segregation into security zones - help protect sensitive information and critical services. Separate administrative network from business processes with physical controls and Virtual Local Area Networks.
References:


