LockBit 2.0 Ransomware
Original Issue Date:-
February 22, 2022
Virus Type:- Ransomware
Severity:-
Critical
It has been reported that the LockBit 2.0 ransomware, which operates as an affiliate-based Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) ramped up its targeted attacks.
Infection Mechanism
LockBit 2.0 is spreading through a variety of techniques, including, but not limited to, purchased access, unpatched vulnerabilities, insider access, and zero day exploits. LockBit 2.0 also developed a Linux-based malware that takes advantage of vulnerabilities within VMWare ESXi virtual machines.
It is also reported that LockBit threat actors are actively exploiting existing vulnerabilities in the Fortinet FortiOS and FortiProxy products, identified as CVE-2018-13379, in order to gain initial access to specific victim networks. After compromising a victim network, LockBit 2.0 actors use publicly available tools such as Mimikatz to escalate privileges. LockBit 2.0 also abuses legitimate tools such as Process Hacker and PC Hunter to terminate processes and services in the victim system.
Prior to encryption, LockBit affiliates primarily use the Stealbit application obtained directly from the LockBit panel to exfiltrate specific file types. LockBit 2.0 features automatic encryption of devices across windows domains by abusing Active Directory group policies. The actor leaves a ransom note in each affected directory within victim systems, which provides instructions on how to obtain the decryption software.

The following are the tools and components that ensure LockBit’s smooth execution:
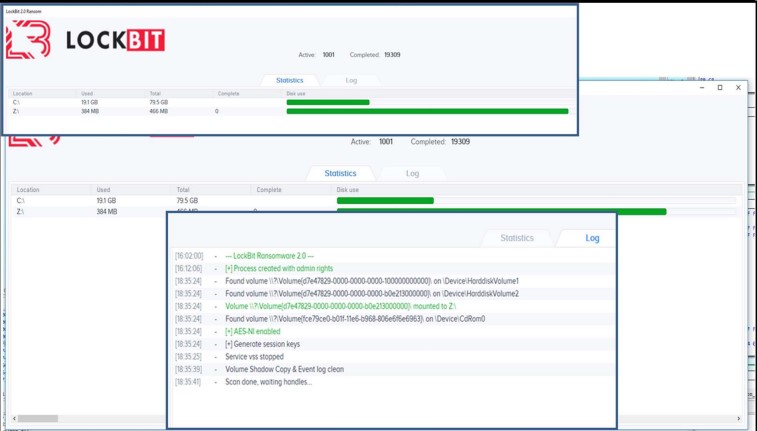
The malware comes with a hidden debug window that can be activated during the infection process using the SHIFT + F1 keyboard shortcut.
Indicator of Compromise:
IP Addresses
- 139.60.160.200
- 93.190.139.223
- 45.227.255.190
- 193.162.143.218
- 168.100.11.72
- 93.190.143.101
- 88.80.147.102
- 193.38.235.234
- 174.138.62.35
- 185.215.113.39
- 185.182.193.120
Hashes (SHA 256)
- 0545f842ca2eb77bcac0fd17d6d0a8c607d7dbc8669709f3096e5c1828e1c049
- 0906a0b27f59b6db2a2451a0e0aabf292818e32ddd5404d08bf49c601a466744
- 21879b5a8a84c5fe5e009c85744caf74b817c57203020bf919037d7ccb6b6a58
- 255f8465962bedaf7a373da5f721aecbc1d6027ca2e4256c6c4352f2de179ca0
- 4db47caf8d93e855b8364def67d3d3282fc964dc4684df6bbe172ea6e902e6fe
- 7b64ca8fe1cace0744a28f43961f17f8ea51910a54d6629502bfb9f3f3e5f831
- 8c0e4a6fd28f94fa17a96f6e424b122f5d1216b230a33c6dff5dbf6654d0721c
- a05ed65787b390ba33b04b4b99c3810cbaf684b37f8839e57db8316e6f01af31
- a26250b8d2431b497400c8a754285a6259a81a31ae629ee25331f6030b34e543
- b09a92dedbcb8d5faed6fcc2194ebaa24da601376b47e1edf705519a7860964e
- bea7aed0dfbf7ce7491d7c8cfed35a2e626fbd345bb7425a34dae6f5894629b1
- cb29c6fbd085407e0e8a58e7cd6512c8c5dfa06f88fdeeb9a66d025fdfc6dd32
- f03584ecdee29e63dee1b7bf2347f605d1e1d6379a8f55e9a85c6a329bf3967b
- 28042dd4a92a0033b8f1d419b9e989c5b8e32d1d2d881f5c8251d58ce35b9063
- 3407f26b3d69f1dfce76782fee1256274cf92f744c65aa1ff2d3eaaaf61b0b1d
- 4bb152c96ba9e25f293bbc03c607918a4452231087053a8cb1a8accb1acc92fd
- 4edbf2358a9820e030136dc76126c20cc38159df0d8d7b13d30b1c9351e8b277
- bcbb1e388759eea5c1fbb4f35c29b6f66f3f4ca4c715bab35c8fc56dcf3fa621
- dd8fe3966ab4d2d6215c63b3ac7abf4673d9c19f2d9f35a6bf247922c642ec2d
- 4db7eeed852946803c16373a085c1bb5f79b60d2122d6fc9a2703714cdd9dac0
- 6876eef67648a3797987745617b9fdfb31a703b7809e7f12bb52c6386e185917
- 717585e9605ac2a971b7c7537e6e311bab9db02ecc6451e0efada9b2ff38b474
- 73406e0e7882addf0f810d3bc0e386fd5fd2dd441c895095f4125bb236ae7345
- 7b5db447f6c29c939f5e0aae1b16431a132db5a2ab4420ba9818af2bf4496d21
- aae5e59d6424515c157f3c4a54e4feeb09759d028290ab0271f730e82f58f10f
- 94e6b969c100483970fc3985bf2b173f2f24d796a079114f584f42484840be28
- a398c70a2b3bf8ae8b5ceddf53fcf6daa2b68af2fadb76a8ea6e33b8bbe06f65
- 98e4c248377b5b62121c7b9ef20fc03df3473cbd886a059998f4210e8df07f15
- a7591e4a248c04547579f014c94d7d30aa16a01bb2a25b77df36e30a198df108
- acad2d9b291b5a9662aa1469f96995dc547a45e391af9c7fa24f5921b0128b2c
- b3faf5d8cbc3c75d4c3897851fdaf8d7a4bd774966b4c25e0e4617546109aed5
- bd14872dd9fdead89fc074fdc5832caea4ceac02983ec41f814278130b3f943e
- d089d57b8b2b32ee9816338e96680127babc5d08a03150740a8459c29ab3ba78
- d089d57b8b2b32ee9816338e96680127babc5d08a03150740a8459c29ab3ba78
- f32e9fb8b1ea73f0a71f3edaebb7f2b242e72d2a4826d6b2744ad3d830671202
- f3a1576837ed56bcf79ff486aadf36e78d624853e9409ec1823a6f46fd0143ea
- 67df6effa1d1d0690c0a7580598f6d05057c99014fcbfe9c225faae59b9a3224
- ee3e03f4510a1a325a06a17060a89da7ae5f9b805e4fe3a8c78327b9ecae84df
Best Practices and Recommendations to protect users against the threat of ransomware:
Users and administrators are advised to take the following preventive measures to protect their computer networks from ransomware infection/ attacks:
- Maintain offline backups of data, and regularly maintain backup and restoration. This practice will ensure the organization will not be severely interrupted, have irretrievable data.
- Ensure all backup data is encrypted, immutable (i.e., cannot be altered or deleted) and covers the entire organization’s data infrastructure
- Implement all accounts with password logins (e.g., service account, admin accounts, and domain admin accounts) to have strong, unique passwords.
- Implement multi-factor authentication for all services to the extent possible, particularly for webmail, virtual private networks, and accounts that access critical systems.
- Remove unnecessary access to administrative shares
- Use a host-based firewall to only allow connections to administrative shares via server message block (SMB) from a limited set of administrator machines
- Enable protected files in the Windows Operating System to prevent unauthorized changes to critical files
- Disable remote Desktop Connections, employ least-privileged accounts. Limit users who can log in using Remote Desktop, set an account lockout policy. Ensure proper RDP logging and configuration
- Check regularly for the integrity of the information stored in the databases
- Ensure integrity of the codes /scripts being used in database, authentication and sensitive system
- Establish Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC), Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM) and Sender Policy Framework (SPF) for your domain, which is an email validation system designed to prevent spam by detecting email spoofing by which most of the ransomware samples successfully reaches the corporate email boxes.
- Keep the operating system third party applications (MS office, browsers, browser Plugins) up-to-date with the latest patches
- Application white listing/Strict implementation of Software Restriction Policies (SRP)to block binaries running from %APPDATA% and %TEMP% paths. Ransomware sample drops and executes generally from these locations.
- Maintain updated Antivirus software on all systems
- Don't open attachments in unsolicited e-mails, even if they come from people in your contact list, and never click on a URL contained in an unsolicited e-mail, even if the link seems benign. In cases of genuine URLs close out the e-mail and go to the organization's website directly through browser
- Follow safe practices when browsing the web. Ensure the web browsers are secured enough with appropriate content controls.
- Network segmentation and segregation into security zones - help protect sensitive information and critical services. Separate administrative network from business processes with physical controls and Virtual Local Area Networks.
- Disable ActiveX content in Microsoft Office applications such as Word, Excel, etc.
- Restrict access using firewalls and allow only to selected remote endpoints, VPN may also be used with dedicated pool for RDP access
- Use strong authentication protocol, such as Network Level Authentication (NLA) in Windows.
- Additional Security measures that may be considered are
- Use RDP Gateways for better management
- Change the listening port for Remote Desktop
- Tunnel Remote Desktop connections through IPSec or SSH
- Two-factor authentication may also be considered for highly critical systems
- If not required consider disabling, PowerShell / windows script hosting.
- Restrict users' abilities (permissions) to install and run unwanted software applications.
- Enable personal firewalls on workstations.
- Implement strict External Device (USB drive) usage policy.
- Employ data-at-rest and data-in-transit encryption.
- Consider installing Enhanced Mitigation Experience Toolkit, or similar host-level anti-exploitation tools.
- Block the attachments of file types, exe|pif|tmp|url|vb|vbe|scr|reg|cer|pst|cmd|com|bat|dll|dat|hlp|hta|js|wsf
- Carry out vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) and information security audit of critical networks/systems, especially database servers from CERT-IN empanelled auditors. Repeat audits at regular intervals.
- Individuals or organizations are not encouraged to pay the ransom, as this does not guarantee files will be released. Report such instances of fraud to CERT-In and Law Enforcement agencies
References:


